Brian Schiff’s Blog
Injury Prevention, Sports Rehab & Performance Training Expert
Increasing shoulder, torso and hip strength and stability is a common training goal for athletes involved in sport. Facilitating hip disassociation and kinetic chain linking with exercise is always a plus. I like to use a diagonal mountain climber with hip extension to accomplish these objectives. More specifically, I utilize this exercise with my overhead athletes and anyone involved in cutting, pivoting and rotational sports.
Begin in a tall plank position. The hands should be beneath the shoulders with the feet on the floor and shoulder width apart. Slowly bring the left knee/hip under the body and toward the right elbow. Pause at the end point prior to losing form or control.
Next, return the left leg toward the start position and up into full hip extension in one continuous movement. Pause at the top end of available hip extension and repeat the cycle for 10 repetitions or time on the same leg. Alternate legs and perform 2-3 sets on each side.
Sufficient upper body strength and core/hip stability in a 3 point position is necessary to perform the exercise correctly. At no time should the foot of the moving leg touch the floor or be used to balance the body. As far as a pace, I feel using a 1/1/1/1 cadence works best.
This exercise is an excellent way to promote shoulder, core and hip stability while facilitating hip disassociation as well. Driving the hip back up into extension will activate the gluteals and simultaneously force the stable (fixed) hip to stabilize the pelvis and counterbalance the movement pattern. In addition, the client will have to effectively activate the hip and abdominal musculature throughout to avoid unwanted pelvic tilt/rotation during the movement.
Click here to view the full video of this exercise I did for my ‘Functionally Fit’ column for PFP Magazine.
Baseball pitchers who fail nonoperative care for SLAP injuries will undergo a repair if they wish to continue throwing. The injury may occur at ball release as the biceps contracts to resist glenohumeral joint distraction and decelerate elbow extension. The other thought is that injury occurs in late cocking as the result of a “peel back” mechanism when the abducted shoulder externally rotates. Previous research by Shepard et al. published in American Journal of Sports Medicine (AJSM) measured in vitro strength of the biceps-labral complex during the peel back and distal force and concluded that repetitive force in both scenarios likely causes SLAP lesions.

“Baseball pitching motion 2004“. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons.
One of the concerns for pitchers after surgery is regaining full shoulder external rotation and horizontal abduction. If too much tension is placed on the glenohumeral ligaments during surgery, regaining motion can be tough. Ironically, external rotation is limited in the early phase of rehab to protect the labral repair which may impair throwing mechanics later on. Appropriate rehab and progression is paramount for long term success.
Laughlin et al. at the ASMI sought out to explore in a labaratory if there are differences in pitchers who underwent a SLAP repair compared to those in age controlled groups without injury. In a paper published in the Dec. 2014 AJSM, the researchers hypothesized that the SLAP group would exhibit compromised shoulder range of motion and internal range of motion torque during pitching. Of 634 pitchers (collegiate and professional) tested at ASMI from 2000 – 2014, 13 in this group were included in the SLAP group as they had undergone a SLAP repair at least 1 year before their biomechanical testing.
All effective prehab and rehab programs for recreational and competitive athletes should include single leg stability exercises. I like to use sliding exercises as one way to improve neuromuscular control of the core, hip and knee. Frontal plane collapse is a common issue with respect to knee dysfunction. Using sliders/gliding discs as well as theraband is an excellent way to improve strength and kinetic chain control. Below is an exercise i recently featured for Personal Fitness Professional:
This exercise is effective in injury prevention and rehab programs for those with ankle instability, anterior knee pain, hip weakness, poor landing mechanics and higher ACL risk if playing pivoting and cutting sports. It will improve core stability, hip and knee strength/stability, dynamic balance, groin flexibility and trunk control.
The band serves to enhance activation of the hip external rotators and further challenge stability of the hip and knee. The band should not pull too forcefully, but just enough to cue the desired muscle activation pattern. A slower cadence on the eccentric portion of the exercise is preferable to maximize stability and strength gains. Do not force through any painful ranges of motion, and remember that form and alignment are paramount so limit the reaching based on the client’s ability to maintain adequate control.
This exercise is an excellent way to increase hip disassociation and more specifically hamstring flexibility. Foam rolling and/or myofascial compression therapy prior to stretching may further enhance range of motion. This exercise can be used with runners and clients struggling with tendonitis, IT band issues and patellofemoral pain. It is also helpful in eliminating asymmetry that appears on the active straight leg raise on the FMS.
This exercise can be used as part of a mobility workout, warm-up, regeneration day or at the end of a workout. Remember that maximally dorsiflexing the foot will increase dural tension and place more stretch across the back of the knee. So, relaxing the foot (or placing the rope more along the mid foot) will reduce this tension and allow for a more concentrated stretch in the hamstring. For clients with a history of sciatica, I would suggest avoiding the stretch with the foot in full dorsiflexion as a general precaution.
I see plenty of pitchers in my clinic ranging from 12 y/o travel baseball players to MLB guys. My own son is a left handed pitcher so I am always carefully watching his mechanics, pitch count and arm care. There has been much written about glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD) and total shoulder motion over the years.
Today, I wanted to recap a nice article that was recently published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine by Wilk et al. looking at deficits in glenohumeral passive range of motion (PROM) and the increase in elbow injury risk.
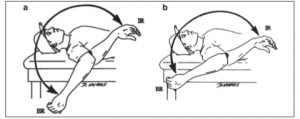
This prospective study was done over an 8 year period from 2005-2102 and looked at PROM of both throwing and nonthrowing shoulders of all major and minor league pitchers within a single baseball organization. The measurements were taken with a bubble goniometer during spring training. See images below from the journal article for how measurements were taken:

In sum, 505 exams were performed on 296 pitchers. Motion was assessed in supine with the arm abducted to 90 degrees and the arm in the plane of the scapula. One examiner stabilized the scapula, while another measured total rotation and passive flexion. Elbow injuries and days missed because of injuries were assessed and recorded by medical staff. Throwing and nonthrowing measurements were compared, while additional testing was done to find significant associations between shoulder motion and elbow injury, as well as odds of an elbow injury.




