Brian Schiff’s Blog
Injury Prevention, Sports Rehab & Performance Training Expert
Shoulder impingement is a common problem for many clients. Specifically, some clients will suffer from internal impingement as a result of a significant loss of internal rotation range of motion, also known as GIRD (glenohumeral internal rotation deficit). This has been widely researched in baseball players, and it is a common issue for overhead athletes. Of note, it can also impact those doing repetitive overhead lifts.
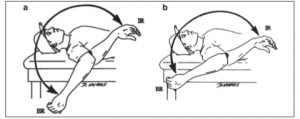
It is common to see asymmetry in internal range of motion for the dominant and non-dominant arms. For those clients who have a total shoulder motion asymmetry greater than 5 degrees, it becomes more important to resolve internal range of motion deficits based on the current literature. In my previous post, I revealed how to improve soft tissue mobility. In this post, I will review the sleeper stretch and cross body stretch to improve posterior shoulder mobility while increasing internal rotation.
The video below from my column ‘Functionally Fit’ for PFP Magazine will demonstrate how to do these stretches.
Spring training has begun, and youth baseball players all over the country are starting to practice and prepare for their upcoming seasons. My very own 14 y/o son has started his 8th grade season, while having been working with his travel team on the weekends since mid December.
As a physical therapist, former player, father, and assistant coach on his 14U team, my first concern is always the health of a player. I see several baseball players in my sports medicine practice ranging in age from 9 year olds to MLB platers. Diagnoses include internal impingement, SLAP tears, little league elbow/shoulder, OCD, UCL sprains, rotator cuff tendinitis, instability, fractures and scapular dyskinesia.
One of the hardest things to do in my profession is get inside the head of a young athlete. Many will refrain from mentioning pain for fear of letting down a parent or coach, or out of concern for losing playing time. Society has become too focused on early specialization and winning from an early age. In addition, “travel baseball” has been somewhat diluted and water down by lots of dads who want their sons to play year-round. I often see kids being abused on terms of too little rest or improper recovery after they pitch and catch.
The biggest, most athletic and hardest throwing kids undergo the most strain as they are asked to shoulder the load at pitcher, catcher and shortstop early on. Many coaches are counting innings in tourneys and not pitches based on tournament guidelines. Too many kids are pitching on consecutive days without proper rest all in an attempt to win meaning less tournaments at a young age. Fortunately, we are making progress in the sports medicine world thanks to the efforts of Dr. James Andrews and others.
High schools are adopting pitch count regulations this year, and MLB along with Dr. Andrews has developed their site, www.pitchsmart.org, to spread education about injury prevention in youth pitchers. Dr. Christopher Ahmad is on the advisory committee for PitchSmart.org, and he is also the lead author on a new paper detailing an injury assessment tool for young baseball players, The Youth Throwing Score.
This is a follow-up from my previous post. Limited thoracic spine rotation can be detrimental for the shoulders, low back and lower extremities with sports and strength and conditioning activity. Consider the impact of asymmetry or stiffness on a golfer, swimmer, thrower, tennis player or even someone doing rotational and pressing working the gym.
Asymmetrical and repetitive activity can lead to deficits as can faulty positions during work and daily life. This simple exercise with the foam roller can be helpful in facilitating optimal mobility and better kinetic chain motion. This video comes from my ‘Functionally Fit’ column for PFP Magazine.

So, I just returned from the Combined Sections Meeting for the APTA that was held in Indianapolis. There was lots of great networking and presentations to be sure. I attended sessions on ACL rehab/prevention, femoroacetabular impingement, elbow injuries in throwers, running gait analysis, and shoulder plyometric training with the legendary George Davies. I thought I would give you my top 10 list of helpful nuggets I picked up over the weekend in no particular order of importance.
1. Performing upper body plyometrics has no effect on untrained subjects so don’t waste time putting it into the rehab program, where as it does benefit trained overhead athletes. The one caveat is it also increases passive horizontal external rotation so keep this in mind when working with athletes who have shoulder instability.
2. A new study coming out in 2015 in AJSM revealed no major differences in throwing kinematics between those following UCL reconstruction (Tommy John) and age-matched controls. This is good news for those worried about pitching mechanics after the procedure.
3. According to Dr. Reiman at Duke, the orthopedic hip exam does a better job of telling us they do not have a labral tear than it does telling us they do have an intra-articular problem. The tests have poor specificity. In fact, he goes on to say that the “special tests are not that special.” That brought a chuckle from the crowd including me. Bottom line – we are not really able to conclusively say “yes you have a labral tear based on my exam today.
4. Reiman also feels we must consider look for mechanical symptoms during the lowering portion of the Thomas test, while considering the fact that fat pad impingement may cause anterior hip pain as opposed to joint pain. Again, things are not always as they appear in the “FAI” crowd so we need to take a great history, look at the classic tests and also see how squatting and loading affects the hip.
5. More experienced pitchers do not drop the glove side arm, but instead tend to move their body toward the glove to conserve angular momentum and overcome small moments of inertia. Less experienced pitchers rotate their trunk sooner in pitching cycles whereas pitchers who threw at higher levels rotated later and produced less torque at the shoulder. Consequently, many players with higher elbow valgus torque and distraction force at the shoulder rotate too early.
I see plenty of pitchers in my clinic ranging from 12 y/o travel baseball players to MLB guys. My own son is a left handed pitcher so I am always carefully watching his mechanics, pitch count and arm care. There has been much written about glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD) and total shoulder motion over the years.
Today, I wanted to recap a nice article that was recently published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine by Wilk et al. looking at deficits in glenohumeral passive range of motion (PROM) and the increase in elbow injury risk.
This prospective study was done over an 8 year period from 2005-2102 and looked at PROM of both throwing and nonthrowing shoulders of all major and minor league pitchers within a single baseball organization. The measurements were taken with a bubble goniometer during spring training. See images below from the journal article for how measurements were taken:

In sum, 505 exams were performed on 296 pitchers. Motion was assessed in supine with the arm abducted to 90 degrees and the arm in the plane of the scapula. One examiner stabilized the scapula, while another measured total rotation and passive flexion. Elbow injuries and days missed because of injuries were assessed and recorded by medical staff. Throwing and nonthrowing measurements were compared, while additional testing was done to find significant associations between shoulder motion and elbow injury, as well as odds of an elbow injury.


