Brian Schiff’s Blog
Injury Prevention, Sports Rehab & Performance Training Expert
I thought a fitting way to kick off the new year would be to share the top 10 things I learned or embraced that have most shpaed and impacted my training and rehab this past year. In no particular order I will rattle these things off. I hope at least one of these little pearls has a positive impact on your training and/or rehab as well.
- Often times it appears necessary to perform a biceps tenodesis or tenotomy in active adults undergoing a SLAP repair to ensure more predictable pain relief. I heard this at a sports medicine conference last May and I can tell you those patients having this done alongside their shoulder surgeries seem to recover quicker with less pain relief. With that said, keep in mind that SLAP tears are difficult to define and operate on as surgeons still do not have great agreement across the board on defining the extent of injuries and how to deal with them (operative vs. non-operative).
- Performance on the Functional Movement Screen (FMS) has little to no correlation with athletic performance. I screened an NBA player and an NFL player this year who both failed the screen. However, they obviously have mad athleticism and genetic ability. Keep in mind the FMS is a valuable tool used to assess movement and expose injury risk patterns based on the 7 tests.
- Soft tissue therapy is undervalued and misunderstood by most lay people. Assessing tissue restrictions and educating our clients to perform self myofascial release techniques is essential if they want to compete and remain healthy day in and day out. Specific problem areas I have increased my focus on this year have been the psoas, soleus and posterior rotator cuff/joint capsule. Click here for my soleus blog post.
- Core training is probably as much about not moving as it is about generating force with movement. I read work from Stuart McGill and other smart people in the field, and the concepts of anti-rotation and anti-extension are sound concepts to explore and look more closely at. Many times, performance in sport and life require us to resist movement and maintain position so strengthening the core to resist potentially harmful and stressful motions is and should be an important part of training and rehab programs. Understanding how to facilitate and activate core musculature in the training to protect the spine and improve mobility/strength is key. Click here for more on my core training.
- Hip dissociation is an important element to train as the lack of it can impact function and performance in a negative way. We assess it on the active SLR in FMS and I see the lack of it show up on clinical exams all the time. Whether it is HS tightness, hip flexor weakness or simply poor neuromuscular control, clients who are unable to effectively dissociate the hips are more prone to injury and limited performance.
Continue reading…
I wanted to take a brief moment to wish all of my readers a Merry Christmas and Happy New Year.

This time of year is one in which to look back and be grateful for all the blessings of the past year, as well as look forward to what the next year has to offer.
2011 has been a time of change as my family and I have embraced our new home in North Carolina. I have thoroughly enjoyed my new position as supervisor and therapist at the Athletic Performance Center. I work with a wonderful staff and a patient population consisting of youth to professional athletes.
As 2012 approaches, I look forward to new opportunities/goals such as becoming board certified in orthopaedic physical therapy, bringing Redcord training to our center as a master trainer, and launching a new program for runners. I hope you have had a great year and I wish you continued health and prosperity in the year to come!
Stay tuned for some pearls of wisdom I will share in my next post about things I have learned and that have most impacted my rehab and training practice over the past year. Thanks for all your questions, support and encouragement – keep it coming. Enjoy the Holidays with your family!
By far the most common problem I see in the clinic is shoulder pain. Most of the time it is related to overuse, rotator cuff tendonitis/impingement and labral tears. Because we are geared more toward sports rehab, I also treat a lot of overhead athletes (baseball players, volleyball players and swimmers).
A common thing I will see in those suffering from impingement or rotator cuff pain is scapular winging. Most of the time the muscle is simply deficient in strength/endurance and it along with the lower trap become overpowered by the upper trap, levator or even the rhomboids. Shortened scapulohumeral muscles, poor posture and pec tightness can also impact winging.
There are many traditional exercises such as serratus punches, push-ups with a plus, and serratus plank push-ups to name a few, but I wanted to include a closed chain exercise that can be very effective for facilitating proper activation of the serratus – quadruped rocking.
In the video, I show it with both hands fixed on the floor progressing to one hand (on the involved side). The key is quality of movement throughout. After you check out the video, be sure to scroll down and click the link to a full column I wrote for PFP magazine on this exercise as it further explains the technique and application.
Click here to read the online column for PFP Magazine.
Well, Thanksgiving is upon us in 2011. I want to wish you and your family a wonderful holiday. In today’s post I will review a November 2011 article in the American Journal of Sports Medicine that looked at the effect of the Nordic hamstring exercise on hamstring injuries in male soccer players.
For those not familiar with Nordic hamstring exercises, see the photo below:
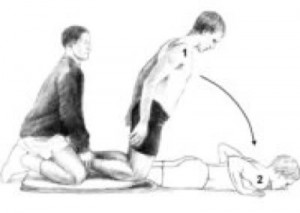
In this randomized trial, the researchers had 54 teams from the top 5 Danish soccer divisions participate. They ended up with 461 players in the intervention group (Nordic ex) and 481 players in the control group. The 10 week intervention program was implemented in the mid-season break between December and and March because this was “the only time of the year in which unaccustomed exercise does not conflict with the competitive season.
The trial was conducted between January 7, 2008 and December 12, 2008 with follow-up of the last injury until January 14, 2009. In the intervention group, all teams followed their normal training routine but also performed 27 sessions of the Nordic hamstring exercises in a 10 week program (as follows)
- Week 1 – 2 x 5
- Week 2 – 2 x 6
- Week 3 – 3 x 6-8
- Week 4 – 3 x 8-10
- Weeks 5-10 – 3 sets, 12-10-8 reps
- Weeks 10 plus – 3 sets 12-10-8 reps
The athletes were asked to use their arms to buffer the fall, let the chest touch the ground and immediately get back to the starting position by pushing with their hands to minimize the concentric phase. The exercise was conducted during training sessions and supervised by the coach. The teams were allowed to choose when in training it was done, but they were advised not to do it prior to a proper warm-up program.
And the results…..
I work with many runners in our clinic. I often see restrictions in the soleus. While the running community is warming up to soft tissue mobilization, many runners are still resistant to embrace it routinely and engage in it more so only when they are hurt or lacking flexibility.
STM (soft tissue mobilization) should be part of every runner’s maintenance program. Why? Simply put, repetitive stress takes its toll on the body. Rolling or releasing the tissue increases blood flow, eliminates trigger points, and facilitates optimal soft tissue mobility and range of motion.
In the diagram below, you can see common trigger points in the soleus. The X represents the trigger point & the red shaded area is the referred pain caused by the trigger point.

In the case of the soleus, restricted dorsiflexion could lead to other biomechanical compensations with running. Initially, this often creates a dysfunctional and non-painful (DN) pattern. Over time, this may eventually become a dysfunctional and painful (DP) pattern forcing runners to seek medical care. The terms DN and DP come from Gray Cook’s Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA).
The gait cycle is certainly altered from dysfunction in this muscle. If ankle joint dorsiflexion is compromised (a common effect of soleus restrictions), there can be increased strain on the quads and altered movement in the hip. Overpronation and excessive hip adduction and internal rotation are common compensations seen with running. Other signs and pathology that may be associated with a soleus trigger point may include:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Heel pain
- Shin pain
- Knee or hip pain
- Back pain
As such, restoring mobility is important. A recent study revealed that immediate improvement in ankle motion can be attained with just a single treatment (click here for the abstract).
So how do you effectively resolve soft tissue issues in this area? I suggest using a foam roller or better yet the footballer and baller block in the Ultimate 6 Kit for Runners by Trigger Point (see pic below)


