Brian Schiff’s Blog
Injury Prevention, Sports Rehab & Performance Training Expert
Rotator cuff tears are common injuries, especially among active middle age men. As researchers and scientists seek for better ways to promote healing and more optimal surgical outcomes, PRP continues to get lots of attention. If you want a basic primer on PRP, click here to read one of my earlier posts on it.
In a recent study in the October 2011 American Journal of Sports Medicine, researchers looked at the effects of PRP on patients undergoing surgery for full thickness rotator cuff tears. This is the first prospective cohort-control study to investigate the effect of PRP gel augmentation during arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Forty two patients were included in the study (average age of 60), with 19 undergoing arthroscopic repair with PRP and 23 without.
Outcomes were assessed preoperatively and at 3, 6, 12, and finally at a minimum of 16 months after surgery (at an average of 19.7 +/- 1.9 months) with respect to pain, range of motion, strength, and overall satisfaction, and with respect to functional scores as determined using multiple assessment tools. At a minimum of 9 months after surgery, repaired tendon structural integrities were assessed by magnetic resonance imaging.
Below are images defining a full thickness rotator cuff tear:

Partial (left) vs. Full (right)
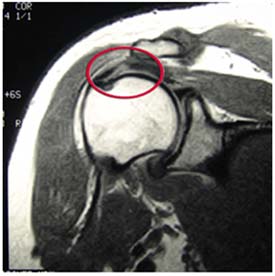
Full Thickness Tear on MRI
I probably get more emails about shoulder problems than anything else. Most of the emails center on rotator cuff and SLAP tears, as well as whether or not to have surgery.
Let me be clear – I am not going to tell you TO or NOT TO have surgery in this post. That is for you and your MD to decide. However, I will give you my thoughts on key considerations with respect to this major decision.
Below are some major considerations to take into account if you are facing this dilemma.
Indications for having surgery:
- Unremitting pain (especially at night)
- Loss of daily function (dressing, bathing, self care activities)
- Marked loss of strength
- Bony impingement with failed rehab
- Moderate to massive tears with active jobs, healthy and < 50 y/0
- Isolated partial and full thickness tears with high probability of operative success after failed rehab
Now, some contraindications for surgery:
- Weakened tissue (including too much tissue retraction or shortening)
- Multiple tears in older population
- Failed previous rotator cuff repair
- High risk patients (includes those with cardiovascular and other medical issues)
- No rehab trial to date
- Partial or full thickness tears with good range of motion, negligible pain and sufficient strength to do most activities of daily living
These thoughts are mostly relative to rotator cuff pathology. SLAP tears are a much different animal in that they often do not do well conservatively with rehab, particularly in active patients. I approach SLAP tears in rehab much like I do a cuff problem, but the varying degrees of SLAP tears and associated involvement of biceps tendon pathology and/or rotator cuff damage make the treatment algorithm more challenging.
What I san say with confidence is that shoulder surgery is never quick and easy. The shoulder is such a complex and pain sensitive joint that whether or not you have arthroscopic or an open repair, the rehab and recovery process is often painful and laborious. This is not to deter you, but more so to make you aware that once you wake up from surgery your shoulder will not be back to normal, nor is there any guarantee your shoulder will be as good as new again. You understand that there is no problem surgery cannot make worse (quote from Dr. Jack Hughston).
Finding a skilled and competent shoulder surgeon will certainly lessen the complications and recovery window. So, when faced with the prospect of surgery, be certain to exhaust conservative measures first, seek multiple MD opinions, get an X-Ray/MRI, and weigh the current functional deficits with the desired functional level to determine the best course of action.

